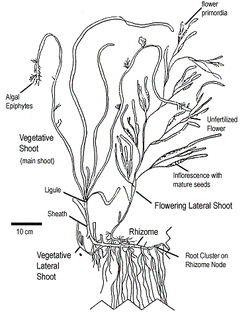
Parts of an Eelgrass Shoot...
Leaf
Much like those of deciduous trees, eelgrass leaves are the primary means of energy production. Eelgrass leaves absorb nutrients directly from the water and can grow to be over 5ft in length.
Rhizome
The rhizome is the horizontal stem of the plant that serves a the backbone from which the leaves and roots emerge. As a shoot grows, the rhizome extends along or just below the sediment surface.
Node
A node is a break in the rhizome that represents a former leafs contention point. Roots or lateral shoots form from the node.
Root
Everyone knows what roots are. They provide nutrient uptake and a means of anchorage to the bottom. With Eelgrass, roots emerge at a slight angle - alternating in direction from one side to the other. Root tips often have root hairs that increase nutrient uptake and strength of anchorage.
Sheath
This is a cellular bundle that holds leaves together. They also encompass and protect the...
Meristem
The meristem is the primary growth point. Leaves grow from terminal meristems, flowers grow from apical meristems. Healthy eelgrass forms a new leaf every two weeks. Damaging a meristem is not good! Everything growing from it usually dies! Unless... the rhizome already branched, forming a new lateral shoot off the main shoot.
Lateral shoot
Lateral shoots form when the rhizome branches. These are important as the shoot they grow out of produces an apical meristem, which flowers then degrades. The lateral shoot, which is still in vegetative growth, supports the flowering lateral shoot.
A single clone of eelgrass -all shoots originate from the same rhizome- live to be thousands of years old! individual shoots do not live for more than two years.
Much like those of deciduous trees, eelgrass leaves are the primary means of energy production. Eelgrass leaves absorb nutrients directly from the water and can grow to be over 5ft in length.
Rhizome
The rhizome is the horizontal stem of the plant that serves a the backbone from which the leaves and roots emerge. As a shoot grows, the rhizome extends along or just below the sediment surface.
Node
A node is a break in the rhizome that represents a former leafs contention point. Roots or lateral shoots form from the node.
Root
Everyone knows what roots are. They provide nutrient uptake and a means of anchorage to the bottom. With Eelgrass, roots emerge at a slight angle - alternating in direction from one side to the other. Root tips often have root hairs that increase nutrient uptake and strength of anchorage.
Sheath
This is a cellular bundle that holds leaves together. They also encompass and protect the...
Meristem
The meristem is the primary growth point. Leaves grow from terminal meristems, flowers grow from apical meristems. Healthy eelgrass forms a new leaf every two weeks. Damaging a meristem is not good! Everything growing from it usually dies! Unless... the rhizome already branched, forming a new lateral shoot off the main shoot.
Lateral shoot
Lateral shoots form when the rhizome branches. These are important as the shoot they grow out of produces an apical meristem, which flowers then degrades. The lateral shoot, which is still in vegetative growth, supports the flowering lateral shoot.
A single clone of eelgrass -all shoots originate from the same rhizome- live to be thousands of years old! individual shoots do not live for more than two years.
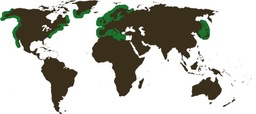
Habitat
[3]
Eelgrass needs abundant light to grow. For this reason it is found only in near shore environments. How deep eelgrass grows depends on the amount of light available and on the clarity of the water. Temperature and salinity also affect eelgrass health.
